Top 10 Industrial Automation Applications for Any Factory
Manufacturers often ask: Where should we start with automation? With tight budgets and limited time, identifying the right first step can make or break your success. The good news? Many of the most common industrial automation applications are also some of the simplest. These applications are ideal for introducing automation in a way that’s cost-effective, low risk, and immediately impactful.
And when the right task is automated, the benefits are hard to ignore.
Shorter lead times. Fewer bottlenecks. More consistent output. Whether it’s packaging, assembly, or machine tending, we’ve seen time and again how even basic automation can free up valuable resources and deliver fast results, especially for small and midsize manufacturers.
Below, we explore 10 practical automation applications found in real factory settings. These are all tasks that can be tackled with off-the-shelf technologies like cobots, vision systems, or even complete plug-and-play robot cells.
Not sure where to begin? Our free, 5-step guide on getting started with automation breaks down how to move from idea to implementation.
Industrial Automation Applications You Can Implement Now:
1. Palletizing in Industrial Automation
One of the most widely adopted applications, palletizing involves stacking boxes, crates, or products onto a pallet at the end of a production line. It’s repetitive, physically taxing, and highly structured. It’s a perfect fit for automation.
Why automate palletizing?
Reduces risk of injury
Handles high throughput without fatigue
Ensures consistent stacking patterns
Entry-level palletizing cells are widely available, with complete solutions starting for less than $18,000. Explore how manufacturers automate palletizing using low-cost, ready-to-deploy systems.
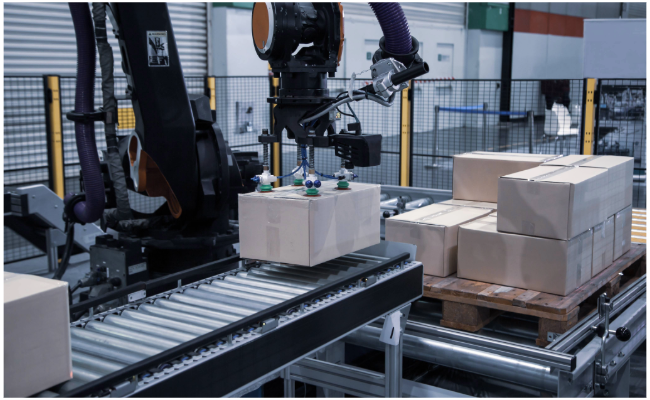

2. How Pick and Place Systems Speed Up Production
Whether you’re moving small parts between stations or transferring finished goods into boxes, pick-and-place automation can significantly reduce cycle times.
Common examples include:
Picking components off a conveyor
Sorting parts into trays
Loading/unloading test equipment
Lightweight cobots and gantry systems for pick and place can be configured online, with entry-level systems available under $9,000.
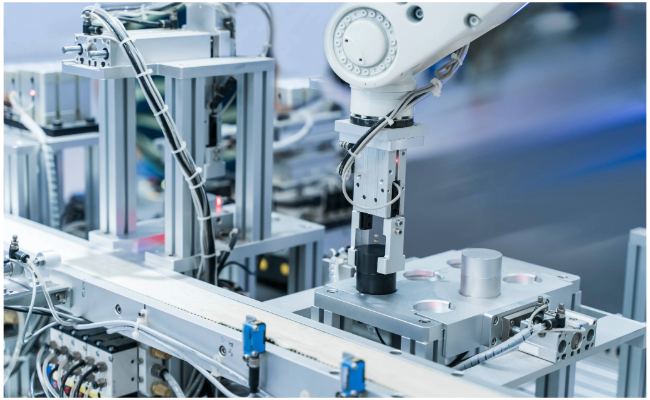

3. Automating Assembly Tasks for Greater Consistency
Robots are increasingly used for precise, repetitive assembly tasks, especially in electronics, automotive, and consumer goods manufacturing.
Typical assembly applications:
Inserting components
Press-fitting
Simple fastening
Affordable options like the igus ReBeL® offer 6-axis flexibility at an entry price point under $8,000. These compact arms make it easy to start automating without needing a six-figure investment.
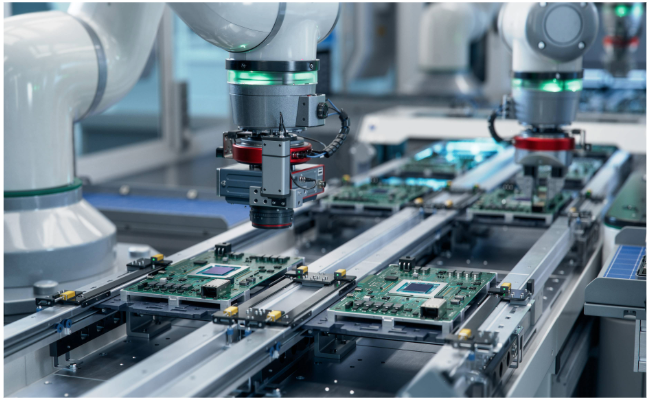
4. Machine Tending: Reducing Downtime with Robots
Machine tending, which is the process of loading and unloading CNC mills, CNC lathes, or injection molding machines, is time-consuming and often inconsistent when done manually.
Benefits of automating this task include:
Better machine utilization
Fewer operator errors
Night shift or lights-out operation
Use our free Machine Planner to configure a CE-compliant robot cell with transparent pricing.
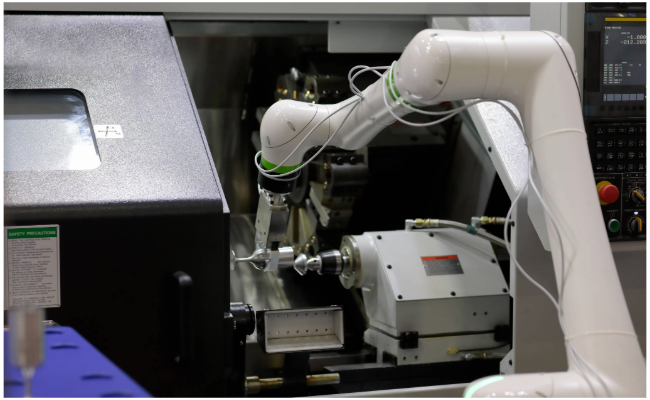
5. Smarter Material Handling on the Factory Floor
Material handling covers a broad range of movements: transferring raw materials, moving work-in-progress, or positioning finished goods.
What makes this task ideal for automation?
It's highly repetitive
Can involve heavy or awkward parts
Often a bottleneck in growing factories
From belt-driven gantries to collaborative carts, there are affordable options even for factories without AGVs or large budgets.

6. Welding Applications for Repeatable Quality
Welding requires precision and consistency, which are both strengths of robotic systems. Automated MIG, TIG, and spot welding cells are becoming more accessible to small manufacturers.
What to automate:
Short, repeatable welds on fixed paths
Fixtures with minimal variation
Tasks in confined or hazardous spaces
Prebuilt welding cells with built-in safety are available on marketplaces like RBTX.com, often priced well below traditional solutions.

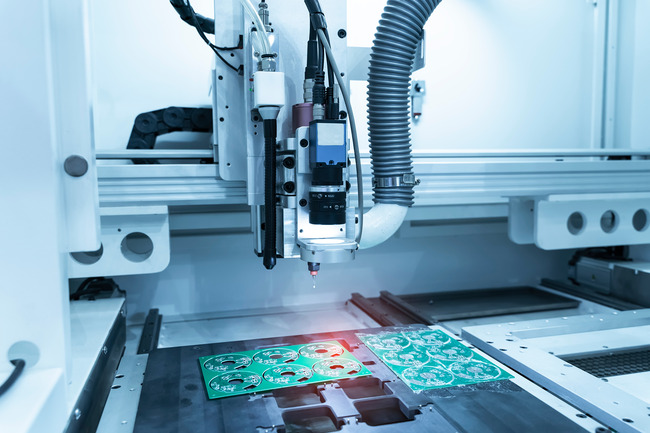
7. Using Vision Systems for Quality Inspection
Vision-based inspection is one of the fastest-growing automation categories. Cameras can now detect surface defects, verify dimensions, and adapt inspections in real time.
Benefits of automating inspection:
100% inline quality checks
Traceable digital records
Non-contact verification
Vision inspection kits integrate easily with cobots, with vision sensors starting under $3,000.
8. Packaging Tasks That Benefit from Automation
Packaging involves several micro-tasks: folding cartons, placing products in trays, sealing bags, all of which are tedious for human workers and easy to standardize.
Start simple by automating:
Tray loading
Box forming or sealing
Bag placing
Configurable packaging cells help reduce ergonomic strain and scale with growing demand.
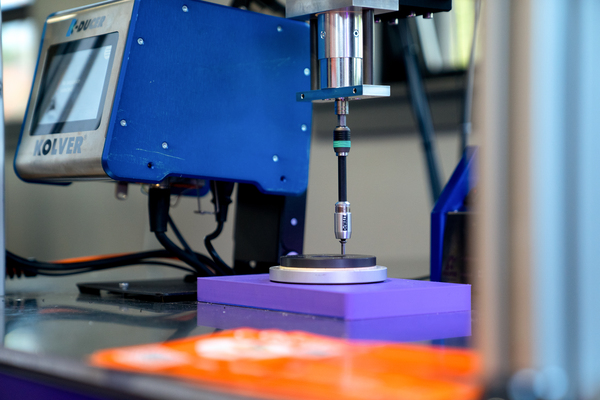
9. Screwdriving Robots in Assembly Lines
Automated screwdriving ensures consistent torque, alignment, and speed, which is critical for quality assurance in electronics, appliances, and metal assemblies.
Common screwdriving uses:
Device enclosures
Panel fasteners
High-mix, low-volume production
Many plug-and-play solutions include integrated torque control and start below $12,000.

10. Dispensing with Accuracy and Efficiency
Dispensing — gluing, sealing, or applying fluids — is another repeatable process that benefits from automation.
Why automate dispensing?
Reduces waste and mess
Improves bead consistency
Handles complex paths with ease
Pre-integrated dispensing kits simplify glue applications and work seamlessly with lightweight robots.
Try our gluing & dosing robot configurator to quickly design a gluing robot tailored to your specific needs.

Why Start with Simple Tasks?
We often tell customers: just start. Automating even one small task builds internal confidence, gets your team comfortable with the tech, and starts paying off quickly.
Many of the tasks above — pick-and-place, palletizing, dispensing — don’t require custom systems or six-figure investments. And with platforms like RBTX, you can:
Compare options from multiple suppliers
Get transparent pricing up front
Access pre-configured robot cells or build your own
Still deciding where to begin? Book a free consultation with one of our automation experts to assess your task and budget.
FAQ: Industrial Automation Applications
What are the most common industrial automation applications? Tasks like palletizing, pick and place, machine tending, and packaging are among the most widely automated because they’re structured and repetitive.
How much does it cost to automate a single task? Entry-level robot arms start under $8,000, while plug-and-play cells for palletizing or screwing can range from $12,000–$18,000.
Can I automate just one process without overhauling everything? Yes. Many factories start by automating just one bottleneck to learn, build buy-in, and grow from there.
What’s the best place to start with automation? Start with something repetitive, rule-based, and easy to define, which is often at the end of a production line. Our Machine Planner tool can help you design a complete solution online.